Polyalthic acid from copaiba oil (derived from Amazon rainforest trees) demonstrates antimicrobial activity without hemolysis in vitro
Polyalthic acid from copaiba oil (derived from Amazon rainforest trees) demonstrates antimicrobial activity without hemolysis in vitro
Polyalthic acid from copaiba oil is an effective antibacterial and should be used to develop alternative medications that can contribute to the effort to overcome antimicrobial resistance ("superbugs"), according to an article by researchers based in Brazil and the United States published in the jou...
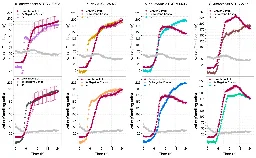
Starter comment: Prior studies of terpenes have shown them to be resilient to the development of bacterial resistance. These new derived compounds demonstrate efficacy against gram positive Staph epidermidis, Staph aureus, and two Enterococci in vitro. Compounds do not require destruction of trees to harvest.
Link to original study: https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6382/12/7/1202