- www.nature.com Stress can disrupt memory and lead to needless anxiety — here’s how
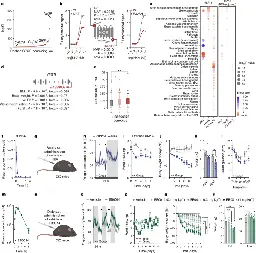
In mice, stress altered the way that the brain formed memories, resulting in an unnecessary fear response.

- www.nature.com Radiation for dummies: the female mannequins testing space-travel safety
The female figures, dubbed Helga and Zohar, took a trip round the moon to measure the levels of space radiation outside low Earth orbit.

- www.nature.com How human brains got so big: our cells learned to handle the stress that comes with size
Understanding how human neurons cope with the energy demands of a large, active brain could open up new avenues for treating neurological disorders.

- www.nature.com Geothermal power is vying to be a major player in the world’s clean-energy future
With technical advances and enthusiasm from policymakers, advocates say the time for next-generation geothermal has come.

-
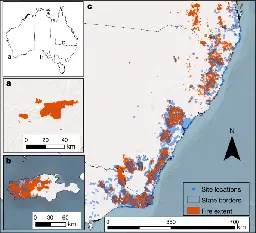
Lunar farside volcanism 2.8 billion years ago from Chang’e-6 basalts
www.nature.com Lunar farside volcanism 2.8 billion years ago from Chang’e-6 basalts - NatureUnravelling the volcanic history of the enigmatic lunar farside is essential for understanding the hemispheric dichotomy of the Moon1-3. Cratering chronology established for the lunar nearside has been used to suggest long-lived volcanism on the farside of the Moon3,4, but without sample verificatio...
- www.nature.com Major biomedical funder NIH poised for massive reform under Trump 2.0
Sweeping changes and more research scrutiny could be on the way for the US National Institutes of Health.

-
Engineered receptors for soluble cellular communication and disease sensing
www.nature.com Engineered receptors for soluble cellular communication and disease sensing - NatureDespite recent advances in mammalian synthetic biology, there remains a lack of modular synthetic receptors that can robustly respond to soluble ligands and in turn activate bespoke cellular functions. Such receptors would have extensive clinical potential to regulate the activity of engineered ther...
- www.nature.com Resistance to crucial malaria drug detected in severely ill kids in Africa
The development worries researchers because children are particularly vulnerable to the disease.

- www.nature.com Daily briefing: Big tomatoes get sweeter thanks to CRISPR editing
A genetic tweak can make big tomatoes much sweeter. Plus, how smartphone signals can help map the upper atmosphere

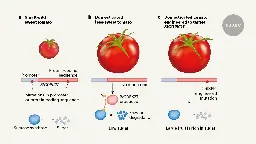
- www.nature.com Tomato engineering hits the sweet spot to make big sugar-rich fruit
Fruit engineered to have high sugar levels without affecting crop yield.
- www.nature.com Why it’s in rich nations’ interests to fund climate finance
Wealthy countries face a stark choice — pay poorer ones to help them decarbonize now or face escalating climate damages at home.

- www.nature.com Huge carnivorous ‘terror bird’ rivalled the giant panda in size
Newly analysed fossil came from what could be the biggest-known member of a family of apex avian predators.

- www.nature.com Why AI-generated recommendation letters sell applicants short
ChatGPT can do many things, but writing a personal endorsement is not one of them, says Maroun Khoury.

-
Trust in scientists starts to recover in the United States at last — but barely
www.nature.com US trust in scientists plunged during the pandemic — but it’s starting to recoverConfidence that scientists will make decisions in the public interest nosedived at the onset of the pandemic but has now started to rise.

- www.nature.com CRISPR builds a big tomato that’s actually sweet
Deleting just two genes that control sugar production makes a more succulent fruit.

-
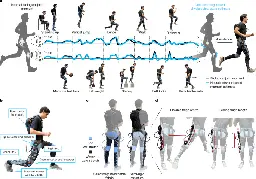
Task-agnostic exoskeleton control via biological joint moment estimation
www.nature.com Task-agnostic exoskeleton control via biological joint moment estimation | NatureLower-limb exoskeletons have the potential to transform the way we move1–14, but current state-of-the-art controllers cannot accommodate the rich set of possible human behaviours that range from cyclic and predictable to transitory and unstructured. We introduce a task-agnostic controller that assis...
- www.nature.com What happens when a bacterium gets into a fungus and stays — for generations
Implanting bacteria into a fungus gives rise to a partnership that evolves over time.

- www.nature.com Space weather mapped by millions of smartphones
A global sensor network for monitoring Earth's ionosphere.

- www.nature.com Can robotic lab assistants speed up your work?
When it comes to laboratory automation, small and simple is the winning combination.

-
Photochemical permutation of thiazoles, isothiazoles and other azoles
www.nature.com Photochemical permutation of thiazoles, isothiazoles and other azoles - NatureThiazoles and isothiazoles are privileged motifs in drug and agrochemical discovery.1,2 The synthesis of these derivatives is generally approached, designed and developed on a case-by-case basis. Sometimes, the lack of robust synthetic methods to a given target can pose significant difficulties or e...
- www.nature.com Bone marrow in the skull plays a surprisingly important role in ageing
Hear the biggest stories from the world of science | 13 November 2024
- www.nature.com Reducing pregnancy risk could be as easy as chewing gum
Clinical trial in Malawi suggests that chewing gum sweetened with the natural compound xylitol is linked to a lower risk of preterm birth.

-
Fluorspar to fluorochemicals upon low-temperature activation in water
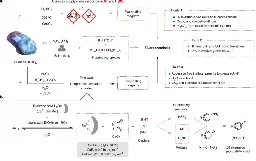
www.nature.com Fluorspar to fluorochemicals upon low-temperature activation in water | NatureThe dangerous chemical hydrogen fluoride sits at the apex of the fluorochemical industry, but the substantial hazards linked to its production under harsh conditions (above 300 degrees Celsius) and transport are typically contracted to specialists. All fluorochemicals for applications, including ref...
-
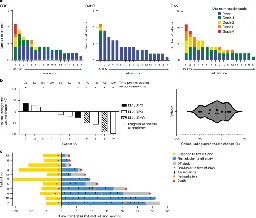
Clinical functional proteomics of intercellular signalling in pancreatic cancer
www.nature.com Clinical functional proteomics of intercellular signalling in pancreatic cancer | NaturePancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has an atypical, highly stromal tumour microenvironment (TME) that profoundly contributes to its poor prognosis1. Here, to better understand the intercellular signalling between cancer and stromal cells directly in PDAC tumours, we developed a multidimensional...

-
Foundation models for fast, label-free detection of glioma infiltration
www.nature.com Foundation models for fast, label-free detection of glioma infiltration | NatureA critical challenge in glioma treatment is detecting tumour infiltration during surgery to achieve safe maximal resection1–3. Unfortunately, safely resectable residual tumour is found in the majority of patients with glioma after surgery, causing early recurrence and decreased survival4–6. Here we ...

-
Prefrontal transthalamic uncertainty processing drives flexible switching
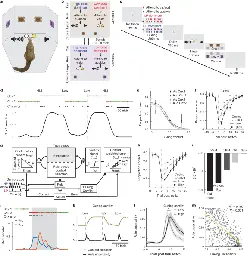
www.nature.com Prefrontal transthalamic uncertainty processing drives flexible switching | NatureMaking adaptive decisions in complex environments requires appropriately identifying sources of error1,2. The frontal cortex is critical for adaptive decisions, but its neurons show mixed selectivity to task features3 and their uncertainty estimates4, raising the question of how errors are attribute...
-
Observation of Hilbert space fragmentation and fractonic excitations in 2D
www.nature.com Observation of Hilbert space fragmentation and fractonic excitations in 2D | NatureThe relaxation behaviour of isolated quantum systems taken out of equilibrium is among the most intriguing questions in many-body physics1. Quantum systems out of equilibrium typically relax to thermal equilibrium states by scrambling local information and building up entanglement entropy. However, ...

-
Mapping the ionosphere with millions of phones
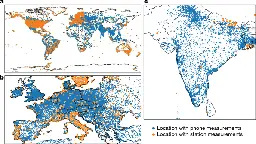
www.nature.com Mapping the ionosphere with millions of phones | NatureThe ionosphere is a layer of weakly ionized plasma bathed in Earth’s geomagnetic field extending about 50–1,500 kilometres above Earth1. The ionospheric total electron content varies in response to Earth’s space environment, interfering with Global Satellite Navigation System (GNSS) signals, resulti...
-
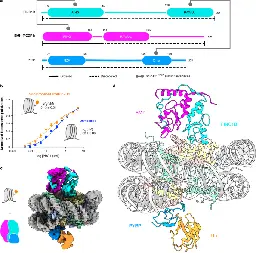
Read–write mechanisms of H2A ubiquitination by Polycomb repressive complex 1
www.nature.com Read–write mechanisms of H2A ubiquitination by Polycomb repressive complex 1 | NatureEpigenetic inheritance of silent chromatin domains is fundamental to cellular memory during embryogenesis, but it must overcome the dilution of repressive histone modifications during DNA replication1. One such modification, histone H2A lysine 119 monoubiquitination (H2AK119Ub), needs to be re-estab...
-
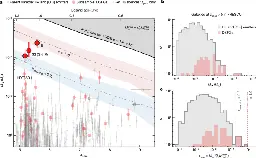
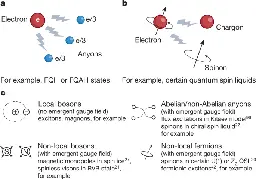
Charge-neutral electronic excitations in quantum insulators
www.nature.com Charge-neutral electronic excitations in quantum insulators | NatureExperiments on quantum materials have uncovered many interesting quantum phases ranging from superconductivity to a variety of topological quantum matter including the recently observed fractional quantum anomalous Hall insulators. The findings have come in parallel with the development of approache...
-
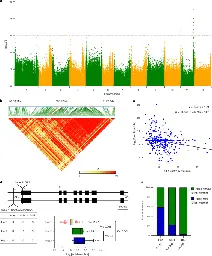
Releasing a sugar brake generates sweeter tomato without yield penalty
www.nature.com Releasing a sugar brake generates sweeter tomato without yield penalty | NatureIn tomato, sugar content is highly correlated with consumer preferences, with most consumers preferring sweeter fruit1–4. However, the sugar content of commercial varieties is generally low, as it is inversely correlated with fruit size, and growers prioritize yield over flavour quality5–7. Here we ...
-
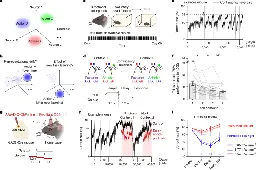
A combinatorial neural code for long-term motor memory
www.nature.com A combinatorial neural code for long-term motor memory | NatureMotor skill repertoire can be stably retained over long periods, but the neural mechanism that underlies stable memory storage remains poorly understood1–8. Moreover, it is unknown how existing motor memories are maintained as new motor skills are continuously acquired. Here we tracked neural repres...
-
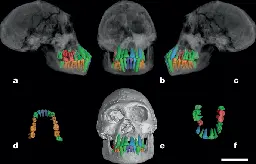
Dental evidence for extended growth in early Homo from Dmanisi
www.nature.com Dental evidence for extended growth in early Homo from Dmanisi | NatureHuman life history is characterized by an extended period of immaturity during which there is a disjunction between cerebral and somatic growth rates1. This mode of ontogeny is thought to be essential for the acquisition of advanced cognitive capabilities in a socially complex environment while the ...
-
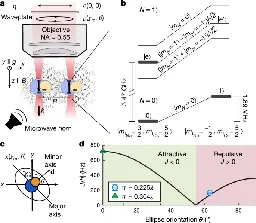
Entanglement and iSWAP gate between molecular qubits
www.nature.com Entanglement and iSWAP gate between molecular qubits | NatureQuantum computation and simulation rely on long-lived qubits with controllable interactions. Trapped polar molecules have been proposed as a promising quantum computing platform, offering scalability and single-particle addressability while still leveraging inherent complexity and strong couplings o...